vCenter sits at the heart of VMware infrastructure, providing a centralized platform for managing and orchestrating virtualized environments. It empowers administrators with comprehensive control over virtual machines, networks, storage, and security, streamlining operations and optimizing resource utilization.
From creating and deploying virtual machines to managing storage and networking resources, vCenter simplifies complex tasks, enabling efficient provisioning, scaling, and maintenance of virtualized workloads. Its robust features cater to various needs, ranging from small-scale deployments to large-scale enterprise environments.
Introduction to vCenter
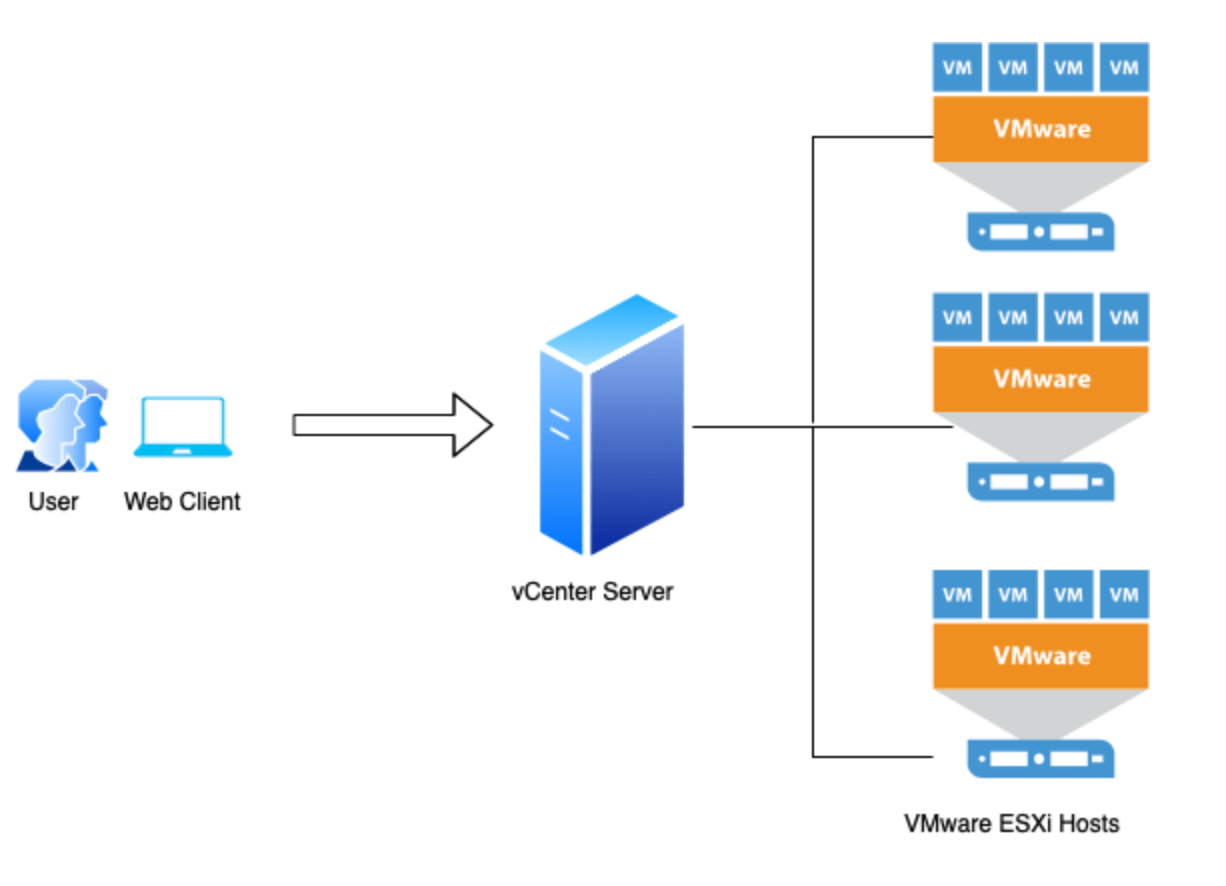
vCenter Server is a centralized management platform for VMware vSphere environments. It acts as the brain of your virtual infrastructure, providing a single point of control for managing virtual machines, hosts, and other components.
vCenter Server offers a wide range of features that simplify the management of virtualized environments, enhance efficiency, and improve overall infrastructure performance.
Key Features and Benefits of vCenter
vCenter Server offers a comprehensive suite of features that streamline virtual infrastructure management. Here are some of the key benefits:
- Centralized Management: vCenter provides a single console for managing all aspects of your vSphere environment, including virtual machines, hosts, storage, and networking. This centralized approach simplifies administration and reduces the time and effort required to manage your infrastructure.
- Enhanced Security: vCenter offers robust security features such as role-based access control (RBAC), encryption, and auditing capabilities. These features help protect your virtual infrastructure from unauthorized access and ensure data integrity.
- Improved Efficiency: vCenter automates many tasks, such as provisioning virtual machines, managing storage, and updating software. This automation reduces manual effort, improves efficiency, and frees up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- High Availability and Disaster Recovery: vCenter provides features like vCenter Server High Availability (HA) and vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) that ensure continuous operation and minimize downtime in the event of failures. This helps maintain business continuity and reduce the impact of outages.
- Advanced Monitoring and Reporting: vCenter offers comprehensive monitoring capabilities, providing real-time insights into the health and performance of your virtual infrastructure. It also generates detailed reports that help identify potential issues and optimize resource utilization.
vCenter Server Editions
vCenter Server is available in several editions, each offering a different set of features and capabilities tailored to specific needs.
- vCenter Server Essentials: This edition is designed for small businesses and organizations with limited virtualization needs. It offers basic management features, including virtual machine provisioning, host management, and basic monitoring.
- vCenter Server Standard: This is the most popular edition, offering a balance of features and capabilities. It includes all the features of Essentials, plus advanced features such as high availability, disaster recovery, and enhanced security.
- vCenter Server Enterprise: This edition is designed for large enterprises with complex virtualization environments. It includes all the features of Standard, plus advanced capabilities such as vSphere Lifecycle Manager (VLM), vSphere Update Manager (VUM), and vSphere Replication.
- vCenter Server Enterprise Plus: This is the most comprehensive edition, offering the full range of vCenter Server features and capabilities. It includes all the features of Enterprise, plus advanced capabilities such as vSphere Data Protection (VDP), vSphere Network Insight, and vSphere vMotion for vSAN.
vCenter Server Architecture
vCenter Server is the central management component of a VMware vSphere environment. It provides a single point of control for managing and monitoring all aspects of your virtualized infrastructure. This section delves into the key components of a vCenter Server deployment and how they interact to ensure seamless operation.
vCenter Server Components
vCenter Server is composed of several interconnected components that work together to provide comprehensive management capabilities.
- vCenter Server: The core component of vCenter Server, responsible for managing ESXi hosts, virtual machines, and other vSphere components. It acts as a central repository for configuration settings, policies, and performance data.
- Platform Services Controller (PSC): A separate component that handles identity management, licensing, and other critical services. It can be deployed as a separate appliance or integrated with vCenter Server.
- vCenter Server Appliance: A virtual appliance that packages vCenter Server and PSC components together, providing a streamlined deployment and management experience.
- ESXi Hosts: The physical servers that host virtual machines. They communicate with vCenter Server to receive management instructions and report their status.
- vCenter Server Database: Stores configuration data, inventory information, and performance metrics. It can be a dedicated database server or embedded within the vCenter Server Appliance.
Interaction between vCenter Server and ESXi Hosts
vCenter Server and ESXi hosts interact through a secure communication channel. ESXi hosts periodically send heartbeat signals to vCenter Server, reporting their status and any changes in the environment. vCenter Server uses this information to monitor the health of the hosts and virtual machines.
- Management and Monitoring: vCenter Server provides centralized management and monitoring capabilities for ESXi hosts, including power management, resource allocation, and performance monitoring.
- Virtual Machine Management: vCenter Server allows administrators to create, deploy, manage, and monitor virtual machines running on ESXi hosts. This includes tasks such as provisioning, cloning, and migrating virtual machines.
- Policy Enforcement: vCenter Server enables the enforcement of policies and security settings across the entire vSphere environment, ensuring consistent configuration and security practices.
- Resource Allocation: vCenter Server optimizes resource allocation by dynamically distributing workloads across ESXi hosts based on predefined policies and resource availability.
vCenter Server Appliance
The vCenter Server Appliance is a virtual machine that packages vCenter Server and PSC components into a single, self-contained unit. This approach simplifies deployment and management, as it eliminates the need for separate installations and configurations.
- Simplified Deployment: The appliance comes pre-configured with all necessary components, making deployment quick and easy.
- Centralized Management: The appliance provides a unified management interface for all vCenter Server components, streamlining administration tasks.
- Enhanced Security: The appliance includes built-in security features, such as firewall and intrusion detection, to protect against unauthorized access.
Platform Services Controller
The Platform Services Controller (PSC) is a separate component that handles critical services like identity management, licensing, and certificate management. It can be deployed as a standalone appliance or integrated with the vCenter Server Appliance.
- Identity Management: The PSC manages user accounts, roles, and permissions, controlling access to vSphere resources.
- Licensing: The PSC manages vSphere licenses, ensuring compliance with VMware licensing agreements.
- Certificate Management: The PSC handles certificate management for vCenter Server and other vSphere components, ensuring secure communication.
Virtual Machine Management with vCenter
vCenter Server provides a centralized platform for managing virtual machines (VMs) within a vSphere environment. It simplifies the creation, deployment, and management of VMs, offering a user-friendly interface and powerful automation capabilities.
Creating Virtual Machines
vCenter Server offers a streamlined process for creating VMs. The process involves defining VM settings, selecting a storage location, and configuring network connectivity.
- VM Settings: This includes defining the VM’s name, operating system, CPU cores, memory, and disk space.
- Storage Location: Choosing the datastore where the VM’s files will be stored.
- Network Connectivity: Specifying the network adapter settings and connecting the VM to the desired network.
Deploying Virtual Machines
Once the VM is created, it can be deployed using various methods.
- Direct Deployment: This involves deploying a new VM from scratch, specifying the necessary settings and configuration.
- Template Deployment: This method utilizes pre-configured VM templates, providing a faster and more consistent deployment process.
- Cloning: Cloning existing VMs allows for quick replication and deployment of identical VM instances.
Managing Virtual Machines
vCenter Server provides comprehensive tools for managing VMs throughout their lifecycle.
- Monitoring: vCenter Server monitors VM performance metrics such as CPU usage, memory consumption, and network activity, providing real-time insights into VM health.
- Resource Allocation: vCenter Server allows for dynamic allocation of resources to VMs based on their requirements and priorities.
- VM Power Management: vCenter Server offers features for powering on, powering off, restarting, and suspending VMs.
- VM Snapshots: Creating snapshots allows for capturing a VM’s state at a specific point in time, providing a rollback mechanism for recovery purposes.
- VM Migration: vCenter Server facilitates live migration of VMs between different hosts, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Virtual Machine Settings and Configurations
vCenter Server offers extensive settings and configurations for customizing VMs to meet specific needs.
- CPU and Memory: Configuring the number of CPU cores, memory size, and CPU allocation policies.
- Storage: Managing disk size, disk type, and storage allocation policies.
- Networking: Defining network adapter settings, network connectivity, and VLAN configurations.
- Operating System: Specifying the operating system type, guest tools installation, and guest operating system customization.
- Security: Configuring security settings, including access control, user permissions, and firewall rules.
Templates and Cloning
Templates and cloning play a crucial role in efficient VM deployment and management.
- Templates: Pre-configured VM images that serve as blueprints for deploying new VMs. They provide a standardized base for VM configurations, ensuring consistency and reducing deployment time.
- Cloning: Creating identical copies of existing VMs, offering a fast and efficient way to deploy multiple instances of a VM. Cloning can be used to create test environments, deploy applications, or quickly scale infrastructure.
vCenter Server for Security and Compliance
vCenter Server plays a critical role in enhancing the security and compliance of your virtualized environment. It provides a comprehensive set of features that enable you to manage access, enforce policies, and monitor activities, ultimately helping you meet regulatory requirements and protect your sensitive data.
Security Features in vCenter Server
vCenter Server offers a wide range of security features designed to safeguard your virtual infrastructure.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): vCenter Server’s RBAC system allows you to define granular permissions for users and groups, ensuring that only authorized individuals can access specific resources. This minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Password Policies: vCenter Server enforces strong password policies for user accounts, requiring users to create complex and unique passwords that are difficult to guess. This helps to prevent unauthorized logins and account takeovers.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): vCenter Server supports 2FA, requiring users to provide an additional authentication factor, such as a one-time code from a mobile device, in addition to their password. This adds an extra layer of security and makes it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
- Secure Shell (SSH): vCenter Server provides a secure channel for remote administration using SSH, encrypting all communication between the client and server. This protects sensitive data and prevents eavesdropping or tampering with network traffic.
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL): vCenter Server uses SSL to encrypt all web traffic, ensuring that data transmitted between the server and clients is secure and confidential. This protects against man-in-the-middle attacks and ensures data integrity.
- Auditing and Logging: vCenter Server provides detailed auditing and logging capabilities, tracking user actions, system events, and security-related incidents. This information can be used to identify potential security threats, investigate incidents, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
vCenter Server for Compliance
vCenter Server assists organizations in meeting compliance requirements by providing tools and features that help to enforce security policies, monitor activities, and generate reports for audits.
- Compliance Reporting: vCenter Server offers comprehensive reporting capabilities that enable you to generate reports on various security-related aspects of your virtual environment, such as user activity, security settings, and compliance status. These reports can be used to demonstrate compliance with regulatory frameworks like PCI DSS, HIPAA, and GDPR.
- Policy Enforcement: vCenter Server allows you to define and enforce security policies, such as password complexity requirements, access control rules, and security hardening settings. This ensures that your virtual environment adheres to your organization’s security standards and industry best practices.
- Vulnerability Scanning: vCenter Server can be integrated with vulnerability scanning tools to identify and remediate security vulnerabilities in your virtual machines. This helps to mitigate risks and ensure that your environment is secure against known threats.
- Security Baseline Configuration: vCenter Server provides templates for configuring security baselines, which define a set of security settings that are considered best practices for your virtual environment. This helps to ensure that your virtual machines are properly secured and compliant with industry standards.
Managing User Permissions and Access Control
vCenter Server’s RBAC system enables you to manage user permissions and access control effectively.
- Roles and Permissions: vCenter Server defines a hierarchy of roles, each with specific permissions that determine what actions users can perform. This allows you to grant appropriate access to different users based on their responsibilities and job functions.
- User Groups: You can create user groups to organize users based on their roles or departments. This simplifies permission management and allows you to assign permissions to groups instead of individual users.
- Object Permissions: vCenter Server allows you to set permissions at the object level, such as virtual machines, datastores, and networks. This enables you to control access to specific resources and prevent unauthorized modifications or deletions.
- Inheritance: vCenter Server supports inheritance of permissions, meaning that permissions assigned to a parent object, such as a datacenter, are automatically inherited by its child objects, such as virtual machines. This simplifies permission management and ensures consistency across your virtual environment.
vCenter Server for Monitoring and Reporting
vCenter Server offers powerful monitoring and reporting capabilities that provide valuable insights into the health, performance, and utilization of your VMware infrastructure. It allows you to proactively identify potential issues, optimize resource allocation, and ensure the smooth operation of your virtualized environment.
vCenter Performance Charts and Graphs
vCenter provides a comprehensive set of performance charts and graphs that visualize key metrics related to your virtual machines, hosts, and other infrastructure components. These charts offer real-time and historical data, enabling you to track performance trends, identify bottlenecks, and diagnose problems.
- Real-time Monitoring: vCenter provides real-time performance data for various metrics, including CPU utilization, memory usage, network throughput, disk I/O, and more. This allows you to monitor the performance of your infrastructure in real time and detect any anomalies or performance issues.
- Historical Data Analysis: vCenter stores historical performance data, enabling you to analyze trends over time. You can use this data to identify patterns, track resource usage, and predict future performance needs.
- Customizable Charts and Graphs: vCenter offers a high degree of customization for charts and graphs. You can select the metrics you want to monitor, define the time frame for data display, and customize the chart appearance to suit your specific needs.
Creating Custom Reports and Dashboards
vCenter allows you to create custom reports and dashboards to gain deeper insights into your infrastructure and address specific needs.
- Custom Reports: vCenter provides a flexible reporting engine that allows you to generate custom reports based on your specific requirements. You can define the data sources, metrics, filters, and report formats to suit your needs. For example, you can create reports to track resource utilization, identify performance bottlenecks, or monitor security events.
- Custom Dashboards: vCenter enables you to create custom dashboards that consolidate relevant performance metrics, alerts, and reports in a single view. You can customize the dashboard layout to display the information you need most, making it easier to monitor your infrastructure at a glance.
- Report Scheduling and Distribution: You can schedule reports to run automatically at regular intervals and distribute them to specific users or groups. This allows you to keep stakeholders informed about the health and performance of your infrastructure without manual intervention.
vCenter Server for Automation and Orchestration
vCenter Server provides a powerful platform for automating tasks and processes within your virtualized environment. This automation capability can significantly streamline operations, reduce manual errors, and improve efficiency. vCenter Server offers a range of tools and features that allow you to automate repetitive tasks, manage complex workflows, and orchestrate various actions across your virtual infrastructure.
vCenter Orchestrator
vCenter Orchestrator is a key component of vCenter Server that enables the automation of tasks and processes. It acts as a workflow engine, allowing you to define and execute complex sequences of actions. vCenter Orchestrator integrates seamlessly with vCenter Server, leveraging its capabilities to automate various aspects of virtual machine management.
Automating Tasks with vCenter Orchestrator
vCenter Orchestrator provides a flexible and powerful framework for automating tasks. Here are some examples of how you can leverage vCenter Orchestrator for automation:
- VM Provisioning: You can automate the process of creating new virtual machines, including tasks like assigning resources, configuring networking, and installing operating systems. This automation streamlines the provisioning process, reduces manual errors, and ensures consistent configurations across virtual machines.
- VM Patching: Patching virtual machines is crucial for security and stability. vCenter Orchestrator can automate the patching process, including identifying required patches, scheduling updates, and applying patches to virtual machines. This automation ensures timely patching and reduces the risk of vulnerabilities.
- VM Backup and Recovery: Regular backups are essential for protecting your virtualized environment. vCenter Orchestrator can automate backup processes, including scheduling backups, selecting backup targets, and performing backups. In case of failures, vCenter Orchestrator can also automate recovery processes, restoring virtual machines from backups.
- Resource Management: vCenter Orchestrator can automate resource management tasks, such as allocating and deallocating resources to virtual machines based on predefined policies. This automation ensures optimal resource utilization and avoids resource contention.
Best Practices for vCenter Server Management
Optimizing vCenter Server performance, security, and stability is crucial for managing your virtualized environment effectively. By implementing best practices, you can ensure a reliable and efficient vCenter Server that meets your business needs. This section will delve into key areas of vCenter Server management, including installation, configuration, performance optimization, security hardening, and maintenance.
Installation and Configuration Best Practices
A well-planned installation and configuration process sets the foundation for a robust vCenter Server. These best practices ensure optimal performance and security:
- Dedicated Hardware: Allocate dedicated hardware resources for vCenter Server, including a powerful processor, ample RAM, and sufficient storage space. This minimizes performance bottlenecks and ensures smooth operation.
- Optimal Operating System: Select a supported operating system version for vCenter Server. Ensure the operating system is up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Database Configuration: Choose a suitable database for vCenter Server, such as SQL Server, Oracle, or PostgreSQL. Configure the database for optimal performance and security, considering factors like disk I/O, memory allocation, and security settings.
- Networking Setup: Configure the network for vCenter Server to provide sufficient bandwidth and security. Use dedicated network interfaces for management traffic, minimizing potential conflicts with other network traffic.
- vCenter Server Appliance Deployment: Consider using the vCenter Server Appliance, a pre-configured virtual appliance, for simplified deployment and management. The appliance offers a streamlined installation process and includes essential components.
Optimizing vCenter Performance and Resource Utilization
Maximizing vCenter Server performance and resource utilization is essential for a responsive and efficient virtual environment. Implement these strategies to optimize vCenter Server performance:
- vCenter Server Appliance Sizing: When deploying the vCenter Server Appliance, select an appropriate size based on your environment’s scale and workload. Larger environments may require a larger appliance with more resources.
- Database Optimization: Regularly monitor and tune the database for optimal performance. Consider factors like database indexes, query optimization, and database caching.
- Network Configuration: Ensure sufficient bandwidth for vCenter Server communication with ESXi hosts and other components. Use dedicated network interfaces for management traffic to avoid network congestion.
- vCenter Server Appliance Resource Allocation: Monitor the vCenter Server Appliance’s resource consumption, including CPU, memory, and disk I/O. Adjust resource allocation as needed to maintain optimal performance.
- vCenter Server Appliance Upgrades: Keep the vCenter Server Appliance up-to-date with the latest patches and updates. Regularly review and upgrade the appliance to benefit from performance improvements and security enhancements.
Maintaining vCenter Security and Stability
Security and stability are paramount for a reliable vCenter Server. Implement these measures to protect your vCenter Server and ensure a secure and stable environment:
- Password Management: Use strong passwords for all vCenter Server accounts and enforce regular password changes. Consider using a password manager to manage and store passwords securely.
- Access Control: Implement robust access control mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC), to restrict access to vCenter Server based on user roles and permissions.
- Security Hardening: Configure vCenter Server security settings to minimize vulnerabilities. Enable security features such as firewall, intrusion detection, and antivirus software.
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up the vCenter Server database and configuration files. Store backups in a secure location, ensuring data integrity and disaster recovery capabilities.
- Security Updates and Patches: Keep vCenter Server, ESXi hosts, and other components up-to-date with the latest security patches and updates. Apply patches promptly to address vulnerabilities and ensure a secure environment.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Implement monitoring tools to track vCenter Server performance, security events, and system health. Regularly review audit logs to identify suspicious activities and security breaches.
Final Review: Vcenter
vCenter is an indispensable tool for organizations seeking to maximize the benefits of virtualization. Its comprehensive capabilities streamline management, enhance security, and optimize performance, empowering administrators to build and maintain robust and scalable virtualized environments.
vCenter is a powerful tool for managing virtualized environments, offering centralized control over your virtual machines. One common application within these environments is email communication, often handled by an exchange server. vCenter can help you monitor the performance of your exchange server, ensuring smooth email flow and efficient resource utilization within your virtualized infrastructure.




