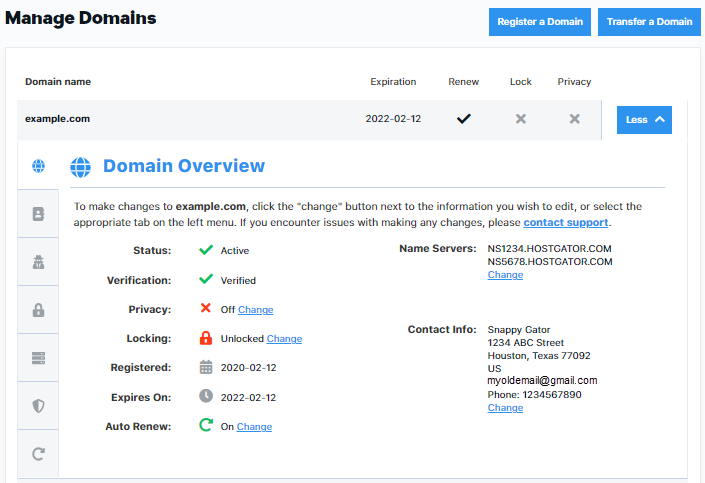
Cloud web hosting has revolutionized the way websites are built and managed. Unlike traditional web hosting, where websites reside on a single server, cloud hosting utilizes a network of servers to distribute resources and provide greater flexibility, scalability, and reliability.
This distributed approach allows websites to handle traffic spikes, avoid downtime, and adapt to changing demands. Cloud hosting offers various types, each tailored to specific needs, from shared hosting for basic websites to dedicated hosting for high-traffic applications.
What is Cloud Web Hosting?
Cloud web hosting is a modern approach to hosting websites, offering several advantages over traditional web hosting. It involves storing your website’s files and data on a network of servers, rather than a single physical server. This distributed infrastructure allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and reliability.
Core Principles of Cloud Infrastructure
Cloud infrastructure relies on a network of interconnected servers, known as a cloud, to provide resources like processing power, storage, and bandwidth. These resources are virtualized, meaning they are presented as separate entities, allowing multiple users to share the same physical infrastructure. This virtualization enables efficient resource allocation and utilization.
Benefits of Cloud Web Hosting
Cloud web hosting offers numerous advantages for website owners, making it an increasingly popular choice.
- Scalability: Cloud hosting allows websites to easily scale up or down based on traffic fluctuations, ensuring optimal performance regardless of user activity.
- Flexibility: Cloud hosting provides flexibility in choosing resources, allowing website owners to customize their hosting environment to meet specific needs.
- Reliability: Cloud hosting distributes data across multiple servers, ensuring redundancy and high availability, even in the event of server failure.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud hosting offers pay-as-you-go pricing models, allowing website owners to pay only for the resources they use, reducing overall costs.
- Security: Cloud providers implement robust security measures to protect data and infrastructure, offering enhanced security for websites.
Types of Cloud Web Hosting
Cloud web hosting offers various options, each catering to specific needs and resources. Understanding the differences between these types is crucial for selecting the right solution for your website.
Shared Hosting
Shared hosting is the most basic and cost-effective option. Multiple websites share the same server resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage. This means that your website’s performance can be affected by the activity of other websites on the same server.
- Pros: Shared hosting is the most affordable option, making it suitable for small websites with low traffic. It is also relatively easy to set up and manage.
- Cons: Shared hosting offers limited resources and performance, making it unsuitable for websites with high traffic or demanding applications. Security can also be a concern, as any website on the server can potentially affect the others.
- Examples: HostGator, Bluehost, GoDaddy
VPS Hosting
VPS (Virtual Private Server) hosting provides a virtualized server environment that is dedicated to your website. You have more control over your server resources, including CPU, RAM, and storage, compared to shared hosting. This means that your website’s performance is less likely to be affected by other websites on the server.
- Pros: VPS hosting offers better performance and security than shared hosting. You have more control over your server environment and can install your own software.
- Cons: VPS hosting is more expensive than shared hosting, but it is still relatively affordable compared to dedicated hosting. It also requires more technical knowledge to manage.
- Examples: DigitalOcean, Linode, Vultr
Dedicated Hosting
Dedicated hosting provides a physical server that is dedicated solely to your website. You have complete control over the server resources and can customize it to meet your specific needs. This is the most powerful and secure option, but it is also the most expensive.
- Pros: Dedicated hosting offers the best performance and security. You have complete control over the server environment and can install any software you need.
- Cons: Dedicated hosting is the most expensive option. It also requires more technical knowledge to manage.
- Examples: Rackspace, AWS, Google Cloud
Cloud Hosting
Cloud hosting is a type of web hosting that uses a network of servers to host your website. This allows for greater scalability and flexibility compared to traditional hosting options. With cloud hosting, you can easily scale your resources up or down as needed, ensuring that your website can handle traffic spikes and growth.
- Pros: Cloud hosting offers high scalability, flexibility, and reliability. It is also cost-effective, as you only pay for the resources you use.
- Cons: Cloud hosting can be more complex to manage than traditional hosting options. It also requires a good understanding of cloud computing concepts.
- Examples: AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure
Comparison Table
| Feature | Shared Hosting | VPS Hosting | Dedicated Hosting | Cloud Hosting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Most affordable | More expensive than shared hosting | Most expensive | Cost-effective, pay-as-you-go |
| Performance | Limited | Better than shared hosting | Best | High, scalable |
| Scalability | Limited | Limited | Limited | Highly scalable |
| Security | Shared security | Improved security | Highest security | Strong security measures |
| Control | Limited control | More control | Complete control | Flexible control |
Advantages of Cloud Web Hosting
Cloud web hosting offers a range of advantages that can significantly benefit businesses and organizations of all sizes. These advantages stem from the inherent flexibility, scalability, and resource-sharing nature of cloud infrastructure.
Scalability
Cloud web hosting allows businesses to easily scale their resources up or down based on their needs. This means that you can add more resources as your website traffic increases, or reduce resources when traffic is low. This dynamic scaling ensures optimal performance and avoids unnecessary costs.
For example, an e-commerce website can easily scale its resources during peak shopping seasons like Black Friday or Cyber Monday to handle the surge in traffic and ensure a smooth shopping experience for customers.
Reliability
Cloud web hosting provides high availability and redundancy, ensuring that your website remains online even if one server fails. Cloud providers typically have multiple data centers and servers, which are interconnected to ensure continuous operation.
Imagine a critical business website experiencing downtime due to server failure. With cloud hosting, the website can seamlessly switch to another server, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
Security
Cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure and employ advanced security measures to protect your data and applications. These measures include firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security audits.
Cloud providers offer a comprehensive security suite that includes data encryption, access control, and regular security updates. This robust security framework minimizes the risk of data breaches and cyberattacks, safeguarding your sensitive information.
Cost-effectiveness
Cloud web hosting can be more cost-effective than traditional hosting, especially for businesses with fluctuating traffic patterns. You only pay for the resources you use, eliminating the need to invest in expensive hardware and infrastructure.
Cloud hosting allows businesses to pay only for the resources they consume, reducing upfront costs and eliminating the need for large capital expenditures. This pay-as-you-go model is particularly beneficial for startups and small businesses with limited budgets.
Table: Cloud Hosting vs. Traditional Hosting
| Feature | Cloud Hosting | Traditional Hosting |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Highly scalable, can easily adjust resources based on demand. | Limited scalability, requires manual intervention to upgrade resources. |
| Reliability | High availability and redundancy, minimizes downtime. | Single server, vulnerable to downtime due to server failure. |
| Security | Robust security infrastructure and measures, protects data and applications. | Security depends on individual configuration, can be vulnerable to attacks. |
| Cost-effectiveness | Pay-as-you-go model, only pay for resources used. | Requires upfront investment in hardware and infrastructure, can be expensive. |
How Cloud Web Hosting Works
Cloud web hosting leverages the power of multiple interconnected servers to host websites, offering a robust and scalable solution compared to traditional single-server hosting. This intricate system relies on various technologies to ensure high availability, performance, and flexibility.
Server Virtualization
Server virtualization is the foundation of cloud web hosting. It allows multiple virtual servers, also known as virtual machines (VMs), to run simultaneously on a single physical server. Each VM has its own operating system and resources, creating isolated environments for different websites. This enables efficient resource utilization and allows for greater flexibility in scaling resources based on demand.
Load Balancing
Load balancing is a crucial aspect of cloud web hosting, ensuring optimal performance and website availability. It distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers, preventing any single server from becoming overloaded. Load balancers act as traffic controllers, directing requests to the most appropriate server based on various factors like server load, availability, and performance. This distribution of traffic prevents bottlenecks and ensures smooth operation even during peak traffic periods.
Data Redundancy
Data redundancy is a vital component of cloud web hosting, safeguarding against data loss. Cloud providers maintain multiple copies of data across different servers in geographically diverse locations. This ensures that even if one server fails, the data remains accessible from other servers. This approach also improves disaster recovery capabilities, as data can be quickly restored from backups in case of unforeseen events.
“Data redundancy is a key principle in cloud computing, ensuring data availability and resilience against failures.”
Cloud Hosting Architecture
The architecture of a cloud hosting environment involves a complex network of interconnected components. A simplified representation can be visualized as follows:
* Clients: Users accessing websites hosted on the cloud.
* Load Balancer: Distributes incoming traffic across multiple servers.
* Virtual Servers: Isolated environments running websites and applications.
* Storage: Stores website files, databases, and other data.
* Network: Connects all components and ensures seamless communication.
* Cloud Provider Infrastructure: Manages and maintains the underlying hardware and software.
Role of Cloud Providers
Cloud providers play a vital role in managing and maintaining the infrastructure that powers cloud web hosting. They are responsible for:
* Hardware Management: Ensuring the physical servers are operational and meet performance standards.
* Software Updates: Keeping the operating systems and applications up-to-date with security patches and bug fixes.
* Network Security: Protecting the cloud infrastructure from cyber threats and ensuring data security.
* Data Backup and Recovery: Maintaining regular backups of data and ensuring swift recovery in case of failures.
* Scalability and Performance: Monitoring and optimizing the cloud environment to ensure optimal performance and scalability.
Choosing the Right Cloud Hosting Provider
Selecting the ideal cloud hosting provider is crucial for ensuring your website’s performance, security, and overall success. With numerous providers offering diverse services, navigating this landscape can be challenging. This section will guide you through the essential factors to consider when choosing a cloud hosting provider.
Factors to Consider
Choosing the right cloud hosting provider involves considering several key factors:
- Pricing: Cloud hosting providers offer various pricing plans, ranging from basic packages to enterprise-level solutions. Evaluate your budget and the features required for your website to determine the most suitable plan. Consider factors such as storage space, bandwidth, and the number of websites you need to host.
- Features: Assess the features offered by each provider, such as website building tools, email accounts, databases, security measures, and scalability options. Ensure the provider offers features that align with your website’s needs and future growth plans.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is essential for resolving any technical issues or addressing concerns. Evaluate the availability and responsiveness of the provider’s support channels, such as live chat, email, or phone. Consider the provider’s reputation for resolving issues promptly and effectively.
- Security: Website security is paramount in today’s digital landscape. Inquire about the security measures implemented by the provider, including firewalls, malware detection, and data encryption. Ensure the provider adheres to industry best practices and complies with relevant security standards.
Questions to Ask Potential Providers
To assess the suitability of a cloud hosting provider, ask these questions:
- What are the different pricing plans and their respective features?
- What level of technical support is available, and how can I contact support?
- What security measures are in place to protect my website and data?
- What is the provider’s uptime guarantee, and how is it monitored?
- What are the options for scaling my website as my traffic grows?
- What is the provider’s reputation for reliability and performance?
- Does the provider offer any free trials or money-back guarantees?
Comparing Cloud Hosting Providers, Cloud web hosting
To compare different cloud hosting providers, consider the following:
- User Reviews: Explore user reviews and testimonials on platforms like G2, Trustpilot, and Capterra to gain insights into the provider’s performance, customer service, and overall experience.
- Industry Rankings: Consult industry rankings and reports from reputable sources such as Gartner, Forrester, and IDC to evaluate the provider’s market standing, capabilities, and customer satisfaction.
- Free Trials: Take advantage of free trials offered by many providers to experience their services firsthand and evaluate their suitability for your needs.
Setting Up a Cloud Web Hosting Account
Setting up a cloud web hosting account is straightforward and often involves a few simple steps. This process allows you to get your website online quickly and efficiently.
Creating a Cloud Web Hosting Account
Creating a cloud web hosting account typically involves choosing a provider, selecting a plan, and setting up your account. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Choose a Cloud Hosting Provider: Select a reputable provider that meets your specific needs. Consider factors like pricing, features, customer support, and scalability.
- Select a Plan: Choose a plan that aligns with your website’s resource requirements. Factors to consider include storage space, bandwidth, and processing power.
- Sign Up and Set Up Your Account: Fill out the necessary information, including your contact details, payment information, and website domain name.
- Configure Your Account: Once your account is set up, you can configure various settings, such as security protocols, email accounts, and database access.
Creating a Website in a Cloud Hosting Environment
Creating a website in a cloud hosting environment typically involves using a website builder, content management system (CMS), or a custom coding approach.
- Website Builders: User-friendly platforms like Wix, Squarespace, or GoDaddy offer drag-and-drop interfaces for building websites without coding knowledge.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Popular CMS platforms like WordPress, Drupal, and Joomla provide flexible frameworks for building and managing dynamic websites.
- Custom Coding: For advanced users, custom coding using languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript offers complete control over website design and functionality.
Transferring an Existing Website to a Cloud Hosting Environment
Transferring an existing website to a cloud hosting environment requires a few steps to ensure a seamless transition.
- Back Up Your Website: Create a complete backup of your website files and database to ensure data safety during the transfer process.
- Create a New Cloud Hosting Account: Choose a cloud hosting provider and set up an account.
- Transfer Your Website Files and Database: Use FTP (File Transfer Protocol) or a similar tool to transfer your website files to the new cloud hosting environment. You can also import your database using tools provided by your cloud hosting provider.
- Update Your Domain Name Settings: Update your domain name’s DNS (Domain Name System) settings to point to your new cloud hosting server.
- Test Your Website: After the transfer, thoroughly test your website to ensure everything is working correctly.
Optimizing Website Performance and Security in a Cloud Hosting Environment
Optimizing website performance and security is crucial for a positive user experience and protecting your website from threats.
- Caching: Implement caching mechanisms to store frequently accessed content, reducing server load and improving website speed.
- Content Delivery Networks (CDNs): Utilize CDNs to distribute website content across multiple servers, minimizing latency and improving website responsiveness.
- Regular Updates: Keep your website software, plugins, and themes up-to-date to patch vulnerabilities and enhance security.
- Strong Passwords: Use strong and unique passwords for your website and hosting account to prevent unauthorized access.
- Security Measures: Implement security measures such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and malware scanning to protect your website from threats.
Cloud Web Hosting for Different Needs
Cloud web hosting is a versatile solution that can cater to a wide range of website needs, from small personal blogs to large enterprise applications. Understanding the specific requirements of your website and how cloud hosting can address them is crucial for choosing the right hosting plan.
Cloud Web Hosting for E-commerce
E-commerce websites require robust infrastructure to handle high traffic volumes, secure transactions, and manage large product catalogs. Cloud hosting provides the scalability and flexibility needed to meet these demands.
- Scalability: Cloud hosting allows e-commerce businesses to easily scale their resources up or down as needed, ensuring smooth operation during peak shopping seasons or promotional campaigns. For example, an online retailer can automatically allocate more resources during Black Friday to handle the surge in traffic and prevent website crashes.
- Security: Cloud providers implement robust security measures to protect sensitive customer data, including payment information. This is crucial for maintaining customer trust and complying with industry regulations.
- Performance: Cloud hosting offers high-performance infrastructure, ensuring fast loading times and a seamless shopping experience for customers.
Cloud Web Hosting for Blogs
Blogs are often content-heavy websites with varying traffic patterns. Cloud hosting offers an efficient and cost-effective solution for bloggers.
- Cost-effectiveness: Cloud hosting allows bloggers to pay only for the resources they use, making it a budget-friendly option, especially for websites with fluctuating traffic.
- Flexibility: Bloggers can easily upgrade their hosting plan as their website grows, without the need for complex server management.
- Reliability: Cloud hosting provides high uptime and redundancy, ensuring that your blog remains accessible to readers even during technical issues.
Cloud Web Hosting for Enterprise Applications
Enterprise applications often require complex integrations, high availability, and strict security measures. Cloud hosting provides the necessary features and resources to support these demanding applications.
- High Availability: Cloud hosting ensures that enterprise applications are always available, minimizing downtime and maximizing productivity.
- Security: Cloud providers offer advanced security features, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and data encryption, to protect sensitive business data.
- Scalability: Cloud hosting allows enterprises to scale their resources up or down as needed, accommodating fluctuations in application usage and ensuring optimal performance.
Cloud Web Hosting Security
Cloud web hosting offers numerous advantages, but security remains a crucial concern. Understanding the potential threats and the security measures implemented by cloud providers is essential for website owners to ensure the safety of their data and applications.
Common Security Threats
Cloud web hosting, like any other online service, is susceptible to various security threats. These threats can target both the cloud provider’s infrastructure and individual user accounts.
- Data breaches: Unauthorized access to sensitive data stored on cloud servers can result in data theft, identity theft, and financial losses.
- Malware infections: Malicious software can infect websites hosted on cloud servers, compromising their functionality and potentially spreading to other websites hosted on the same infrastructure.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: These attacks aim to overwhelm cloud servers with traffic, making websites unavailable to legitimate users.
- Misconfigurations: Incorrect security settings or configurations on cloud servers can create vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
- Insider threats: Employees or contractors with access to cloud infrastructure can potentially misuse their privileges to compromise security.
Security Measures Implemented by Cloud Providers
Cloud providers implement various security measures to protect user data and websites. These measures include:
- Physical security: Data centers housing cloud servers are equipped with physical security measures such as surveillance systems, access control, and environmental monitoring.
- Network security: Firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other network security tools are deployed to prevent unauthorized access and malicious traffic.
- Data encryption: Sensitive data stored on cloud servers is typically encrypted at rest and in transit to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Regular security audits: Cloud providers conduct regular security audits to identify and address potential vulnerabilities.
- Security monitoring: Cloud providers constantly monitor their infrastructure for suspicious activity and potential security breaches.
Website Owner Security Measures
Website owners can further enhance the security of their cloud hosting by implementing additional measures:
- Strong passwords: Use strong, unique passwords for all cloud hosting accounts and websites.
- Two-factor authentication: Enable two-factor authentication for all cloud hosting accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Regular software updates: Keep all software, including operating systems, web applications, and plugins, up to date to patch security vulnerabilities.
- Security plugins: Install security plugins on websites to enhance protection against malware and other threats.
- Regular backups: Create regular backups of website data to ensure recovery in case of a security breach.
The Future of Cloud Web Hosting

The cloud web hosting landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user demands. Several key trends are shaping the future of cloud web hosting, promising to enhance performance, scalability, and security while opening up new possibilities for businesses and individuals.
Impact of Edge Computing and Serverless Computing
Edge computing and serverless computing are two transformative technologies that are poised to significantly impact the future of cloud web hosting.
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to users, reducing latency and improving performance. This is particularly beneficial for applications that require real-time data processing or low latency, such as gaming, streaming, and IoT devices. Cloud hosting providers are increasingly integrating edge computing capabilities into their platforms, offering users the ability to deploy applications and services closer to their target audience.
Serverless computing, on the other hand, allows developers to run code without managing servers. This eliminates the need for infrastructure provisioning and management, allowing developers to focus on building applications. Serverless functions can be scaled automatically based on demand, making them ideal for applications with unpredictable traffic patterns. Cloud hosting providers are offering a wide range of serverless computing services, enabling businesses to build and deploy applications more efficiently and cost-effectively.
Emerging Use Cases for Cloud Web Hosting
Cloud web hosting is becoming increasingly relevant for a wider range of use cases, beyond traditional website hosting.
Mobile App Hosting
Cloud hosting is becoming the preferred platform for hosting mobile apps. Cloud platforms offer the scalability and flexibility needed to handle the increasing demand for mobile apps, while also providing features like push notifications, user authentication, and data storage.
Internet of Things (IoT) Device Hosting
As the number of connected devices continues to grow, cloud hosting is becoming essential for managing and processing data from IoT devices. Cloud platforms offer the scalability and security needed to handle the large volumes of data generated by IoT devices, while also providing tools for data analysis and visualization.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Hosting
Cloud hosting is becoming an integral part of AI and ML development and deployment. Cloud platforms offer the computational power and storage capacity needed to train and run AI models, while also providing tools for data management, model deployment, and API integration.
Conclusion

As technology continues to evolve, cloud web hosting remains at the forefront, offering a dynamic and adaptable platform for businesses and individuals alike. By leveraging the power of cloud infrastructure, websites can achieve optimal performance, security, and scalability, paving the way for a seamless online experience.
Cloud web hosting offers a flexible and scalable solution for businesses of all sizes. One often overlooked aspect of cloud infrastructure is the ability to integrate peripheral devices, such as a print server , seamlessly. This allows for centralized print management, eliminating the need for dedicated hardware and simplifying document workflows, ultimately enhancing the overall cloud hosting experience.